The Language Every Trader Must Speak
Trading isn’t just about numbers — it’s a language of its own. That’s why this Trader’s Dictionary was created — to help you understand the terminology that drives every trade, every strategy, and every analysis. Learning these forex trading terms is the first step toward mastering the markets.
1. Forex — The World’s Largest Financial Market
In this Trader’s Dictionary, Forex refers to the global marketplace where currencies are exchanged across the world.
Forex (Foreign Exchange) is where currencies are traded globally. It’s the largest and most liquid financial market, with a daily turnover exceeding $7.5 trillion.
Unlike the stock market, Forex operates 24/5 and is decentralized — meaning there’s no single exchange. Instead, transactions occur electronically between banks, brokers, and traders worldwide.

2. Currency Pair
A currency pair shows the value of one currency relative to another.
- The base currency is the first (e.g., EUR/USD → EUR).
- The quote currency is the second (e.g., USD).

If EUR/USD rises, it means the euro strengthens against the dollar. Traders can go long (buy) or short (sell) depending on their market outlook.
3. Leverage
Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. For example, with 1:100 leverage, you can control $100,000 using just $1,000.
However, leverage amplifies both profits and losses — making risk management critical.
⚠️ Tip: Always trade with a risk plan. High leverage can quickly magnify mistakes.
4. Margin
Margin is the collateral your broker requires to open a trade. It ensures you have enough capital to cover potential losses. Margin is not a fee — it’s a deposit held while your trade is active.
5. Lot
A lot represents a standardized quantity in trading.
- Standard lot = 100,000 units of the base currency
- Mini lot = 10,000 units
- Micro lot = 1,000 units
At DAK Markets, you can trade using micro lots to manage risk with precision.
6. Pip
A pip (Percentage in Point) measures the smallest price movement in Forex — typically 0.0001.
If EUR/USD moves from 1.1000 to 1.1005, that’s a 5-pip increase.
7. Bid, Ask & Spread
- Bid: Price buyers are willing to pay
- Ask: Price sellers want to receive
- Spread: The difference between bid and ask prices — it represents your trading cost.
Tighter spreads = lower costs. That’s why DAK Markets focuses on offering raw spreads starting from 0.0 pips.
8. Long & Short Positions
- Long position: Buying an asset expecting its price to rise.
- Short position: Selling an asset expecting its price to fall.
Professional traders profit in both rising and falling markets — it’s about timing and direction, not luck.
9. Market, Limit & Stop Orders
- Market Order: Executes immediately at the best available price.
- Limit Order: Executes only at a specific or better price.
- Stop Order: Triggers when price moves beyond a certain point, following the trend.
These tools give you control over when and how your trades open or close.
10. Stop Loss, Take Profit & Trailing Stop
- Stop Loss (SL): Automatically closes a trade to prevent excessive losses.
- Take Profit (TP): Locks in profits at a chosen level.
- Trailing Stop: Dynamically follows the price to secure profits as the market moves in your favor.
Risk management is what separates consistent traders from gamblers — every DAK Markets professional uses these tools effectively.
11. Candlestick Chart
Candlestick charts visualize price movements — each candlestick shows the open, close, high, and low for a chosen time period.
Green candles indicate rising prices; red candles, falling prices.
Understanding candle patterns is key to technical analysis — something our DAK Markets Education Hub covers in depth.

12. Volatility
Volatility measures how much an asset’s price fluctuates.
- High volatility = large price swings = greater profit potential but higher risk.
- Low volatility = slower movement = safer but smaller returns.
Traders love volatility — it’s where opportunity lives.
13. Broker
A broker connects traders to the financial markets. At DAK Markets, we provide:
- Institutional liquidity
- Fast trade execution
- Raw pricing
- Advanced trading platforms like cTrader
Your broker is your gateway — make sure it’s one you trust.
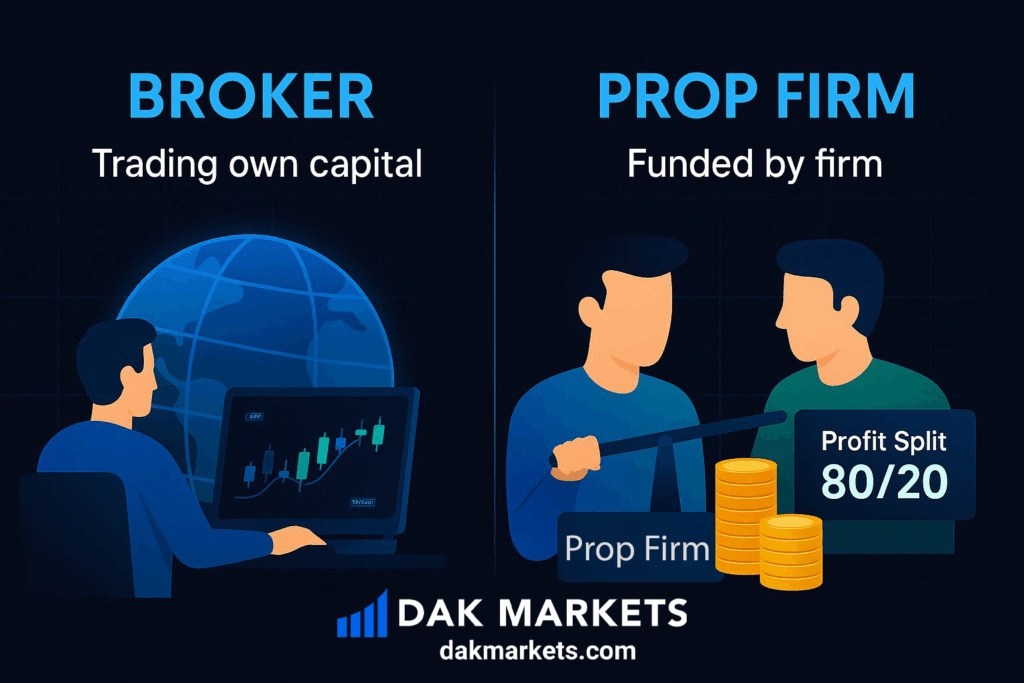
14. Prop Trading vs. Retail Trading
Prop trading firms fund traders with company capital after passing an evaluation.
Retail brokers like DAK Markets provide traders access to real markets with their own deposits.
Many professionals start with brokers to build experience, then expand into prop trading for higher capital access.
Final Thoughts
Every successful trader began as a beginner who took time to learn the basics. Understanding these key terms will help you interpret charts, manage risk, and communicate like a professional.
This Trader’s Dictionary is designed to make complex forex trading terms easy to understand for every trader.
At DAK Markets, we don’t just offer trading platforms — we offer education, community, and the tools to grow.
✅ Start Your Journey Today
📈 Open your live trading account or demo account at www.dakmarkets.com
🎓 Visit our Education Hub to learn more
💬 Contact our support team for help anytime